
Diamond Microdermabrasion Machine
The following table contains a selection of minerals gemologists may encounter as jewelry stones or gem specimens. The gems are sorted by their crystal system: cubic (isometric), tetragonal, hexagonal, trigonal, orthorhombic, monoclinic, and triclinic. These butterscotch-colored wulfenite gemstones show their tetragonal crystal structure.
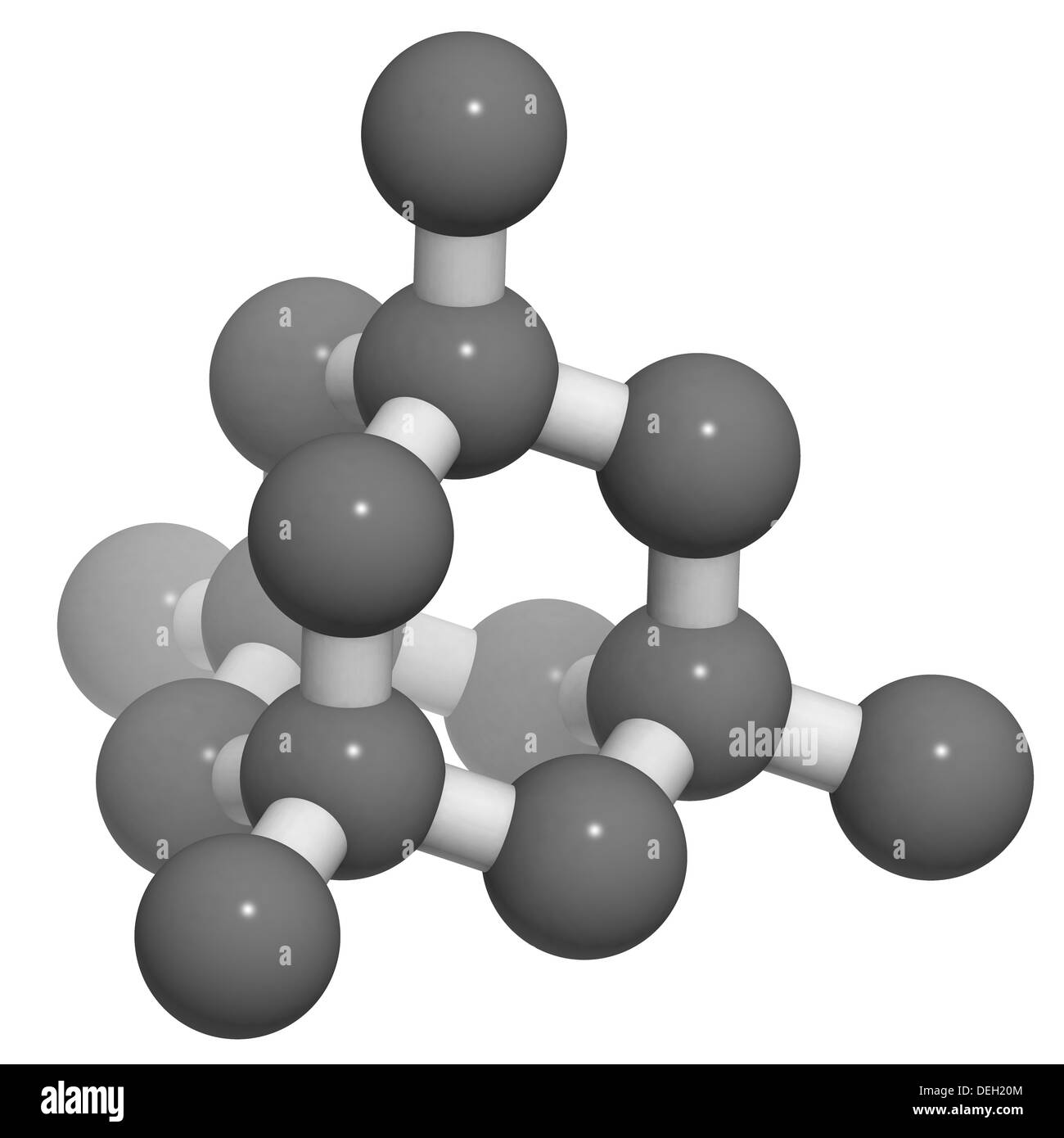
Diamond crystal structure. Unit cell. Unbound atoms omitted. Atoms Stock Photo 60611060 Alamy
Diamond belongs to the cubic crystal system, which is the most symmetrical of crystal systems. The basic crystal shape, or habit, of diamond is the octahedron; a form with eight equal triangular sides, looking like two pyramids connected at the base. Octohedrons from the Mir Mine in Russia. Other shapes of diamonds are the cube (6 equal square.
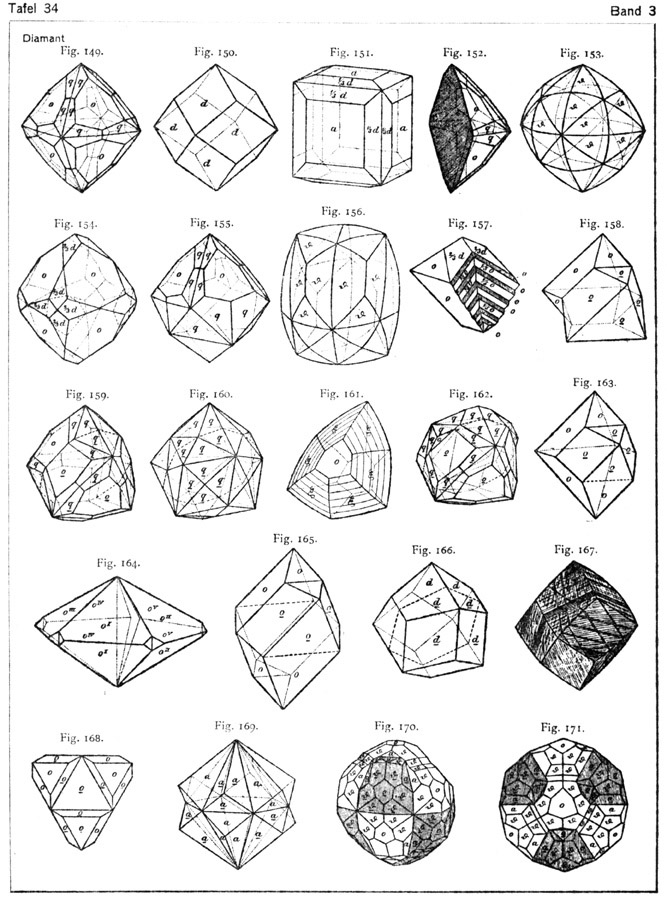
Diamond Crystal Diagrams from Goldschmidt's Atlas der Krystalformen
The crystal structure of a diamond is a face-centered cubic or FCC lattice. Each carbon atom joins four other carbon atoms in regular tetrahedrons (triangular prisms). Based on the cubic form and its highly symmetrical arrangement of atoms, diamond crystals can develop into several different shapes, known as 'crystal habits'.

Diamond Crystal Structure YouTube
August 19, 2022 When you first start learning about diamonds, you will discover that these carbon-based gems belong to the cubic crystal system. Diamonds can be unearthed in numerous forms that belong to this system. Here, Gem-A Gemmology Tutor Pat Daly explains more about the shapes of diamonds.

Diamond Cubic Crystal Structure YouTube
DOI: 10.1038/s41550-023-02147-x. An international team of researchers led by Dr. Mungo Frost from the SLAC research center in California has gained new insights into the formation of diamond rain.
EJM How do diamonds grow in metal melt together with silicate minerals? An experimental study
DIAMOND features a split-screen format with the left portion of the screen serving as the structure window and the right portion being a `data sheet' containing useful crystallographic information such as crystal system and space group, lattice dimensions, atomic coordinates, vibrational displacement parameters and selected geometric parameters.

Diamond (gemstone)
Diamond is a solid form of pure carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal. Solid carbon comes in different forms known as allotropes depending on the type of chemical bond. The two most common allotropes of pure carbon are diamond and graphite.

Diamond is in the isometric crystal system, which is reflected in the usually found octahedral
Diamond is the allotropic form of carbon and the space lattice of the diamond is face centered cubic (FCC) and two atoms in the basis. The Bravais Lattice It is implemented to characterize the crystals without any imperfections and defects, and they have regular atomic arrangements.

A+ Herkimer Diamond Crystal Point Golden Healer Aura *Solar Quartz* New York Diamond Quartz
The diamond type classification system is widely used in diamond research, because it provides a convenient way to categorize diamonds based on their chemical and physical properties. Understanding this system is critical to evaluating the relationships between dia-mond growth, color (e.g., figure 1), and response to laboratory treatments.

Diamond crystal structure illustration Stock Vector Image by ©Dr.PAS 6327589
This crystal system has the lowest symmetry and must be described by 3 lattice parameters (a, b, and c) and the 3 angles (α, β, and γ). Atom Positions, Crystal Directions and Miller Indices. Atom Positions and Crystal Axes.. The diamond cubic structure consists of two interpenetrating face-centered cubic lattices, with one offset 1/4 of a.

Meet Diamond Crystal CanvasRebel Magazine
The diamond derives its name from the Greek adamas, "untameable" or "unconquerable", referring to its hardness. Diamonds typically crystallize in the cubic crystal system and consist of tetrahedrally bonded carbon atoms. A second form called lonsdaleite with hexagonal symmetry is also found. The local environment of each atom is identical in.

Scientists Make a Breakthrough Towards Solving the "Grand Scientific" Structural Mystery of Glass
Modified date: 25/09/2023 Diamonds are one of the most precious and valuable gemstones in the world, known for their exceptional hardness, brilliance, and durability. They are formed deep within the earth over millions of years under intense heat and pressure, and are typically found in kimberlite pipes or alluvial deposits. Quartz Herkimer Diamond
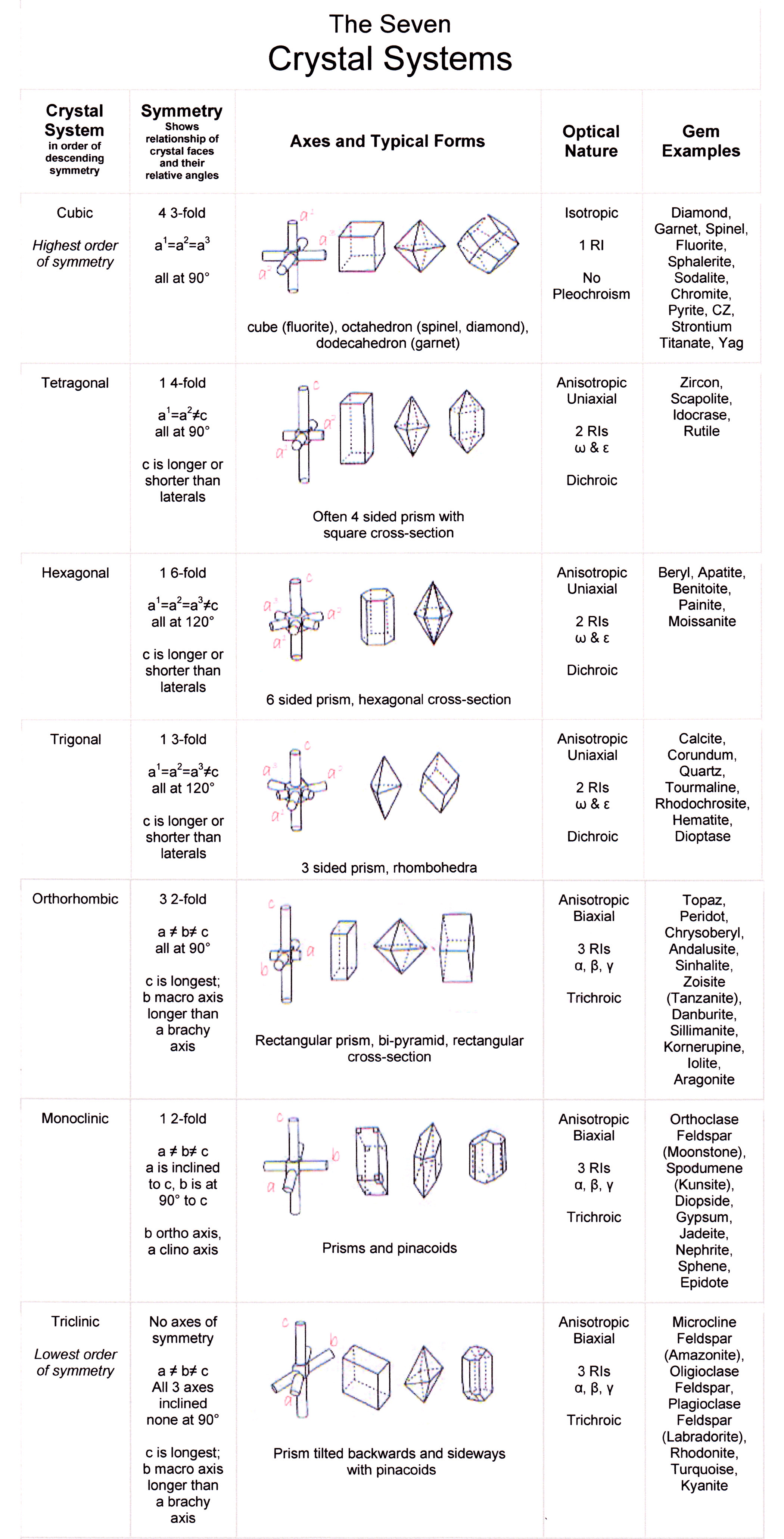
RevisedSevenCrystalSystems Diamond
Crystallographic structure Visualisation of a diamond cubic unit cell: 1. Components of a unit cell, 2. One unit cell, 3. A lattice of 3 × 3 × 3 unit cells Diamond's cubic structure is in the Fd 3 m space group (space group 227), which follows the face-centered cubic Bravais lattice.
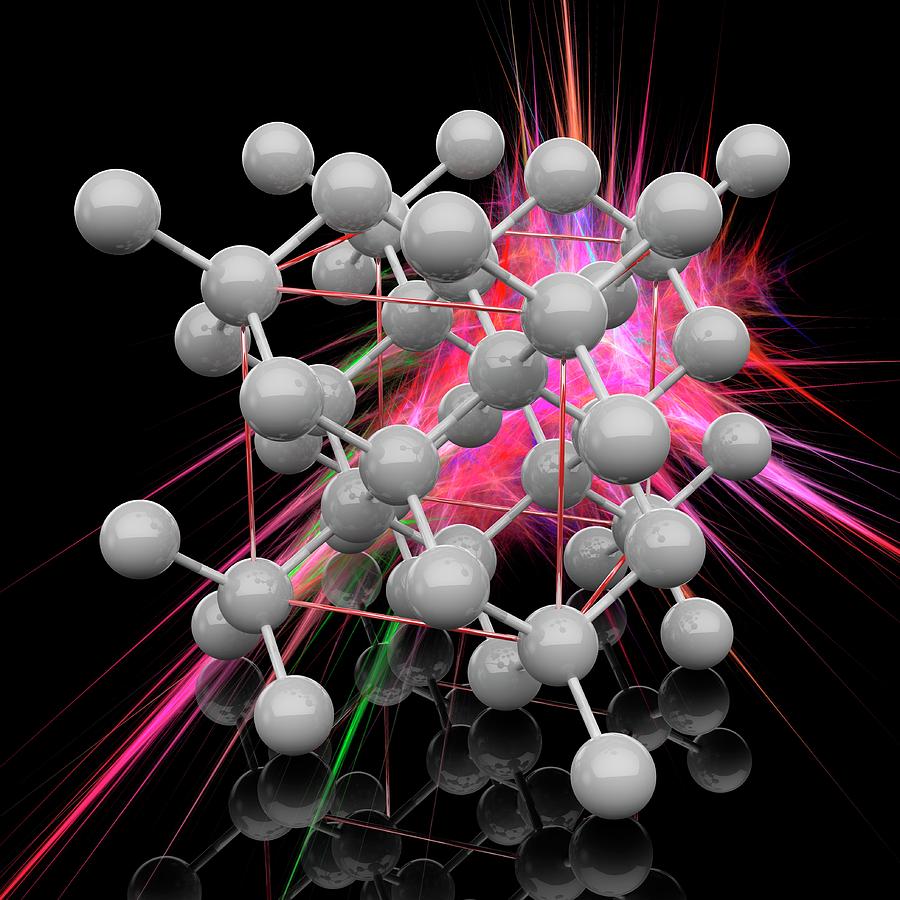
Diamond Crystal Structure Photograph by Laguna Design/science Photo Library Pixels
Hardness and crystal structure. Known to the ancient Greeks as ἀδάμας (adámas, 'proper, unalterable, unbreakable') and sometimes called adamant, diamond is the hardest known naturally occurring material, and serves as the definition of 10 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness.Diamond is extremely strong owing to its crystal structure, known as diamond cubic, in which each carbon atom.

Diamond Crystal
The diamond {111} peak is well suited to determine the presence of diamond as the diamond anvils are single crystals with the (100) axis aligned with the compression axis (and the XFEL beam), so.

L’ère des diamants faits en laboratoire Québec Science
Abstract. Self-assembling colloidal particles in the cubic diamond crystal structure could potentially be used to make materials with a photonic bandgap 1, 2, 3. Such materials are beneficial.